Apache Spark on Marc: Difference between revisions
Created page with "= Overview = This guide gives an overview of running Apache Spark clusters under the existing scheduling system of the Level 3/4 Rated Marc cluster at the University of Calga..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* This message says that the Jupyter server is running on node sg5 on port 54674. Port 8888 needs to be forwarded from the server running Putty to the cluster. | * This message says that the Jupyter server is running on node sg5 on port 54674. Port 8888 needs to be forwarded from the server running Putty to the cluster. | ||
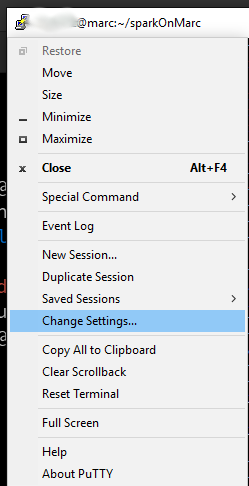
* Click the Putty icon in the upper left corner of the Putty window and select "Change Settings" | * Click the Putty icon in the upper left corner of the Putty window and select "Change Settings" | ||
[[File:ChangeSettings.png|alt=Image showing where the "Change Settings" option for Putty is located|none|thumb|Image showing where the "Change Settings" option for Putty is located]] | |||
* If there's already 8888 listed in the Forwarded ports box click it and click Remove -- the Forwarded ports box should be empty. | * If there's already 8888 listed in the Forwarded ports box click it and click Remove -- the Forwarded ports box should be empty. | ||
* In the Change Settings dialogue box pick "Tunnels" in the left hand box (you'll have to open the Various levels of the tree to get there) | * In the Change Settings dialogue box pick "Tunnels" in the left hand box (you'll have to open the Various levels of the tree to get there) | ||
* Enter 8888 into the Source port box | * Enter 8888 into the Source port box[[File:SettingsDialogueBox.png|alt=Putty Settings dialogue box showing the required port forwarding.|none|thumb|Putty Settings dialogue box showing the required port forwarding.]] | ||
* Copy the circled value from the putty window into the Destination box and click the Add button. | * Copy the circled value from the putty window into the Destination box and click the Add button. | ||
* The "Forwarded ports" box should now contain a concatenation of the text in the source port and destination boxes. i.e. "8888:sg4:54674" | |||
* Click Apply | * Click Apply | ||
* Return to the myappmf tab in your browser and start a Google Chrome there. '''Note:''' It is important that you use the Chrome from myappmf not your desktop. | * Return to the myappmf tab in your browser and start a Google Chrome there. '''Note:''' It is important that you use the Chrome from myappmf not your desktop. | ||
* Paste the link containing http://localhost:8888?token= into | * Paste the link containing http://localhost:8888?token= found in the putty terminal window into the browser started from myappmf and you should be rewarded with a Jupyter Notebook session. | ||
In your Python file or terminal load the appropriate python modules and instantiate the cluster: | In your Python file or terminal load the appropriate python modules and instantiate the cluster: | ||
Revision as of 17:54, 29 June 2022
Overview
This guide gives an overview of running Apache Spark clusters under the existing scheduling system of the Level 3/4 Rated Marc cluster at the University of Calgary.
Due to certain mandatory security restrictions required when accessing Level 3 and 4 data, we are not able to provide access to Sparc via Open On Demand as it is done on Arc. There is a slightly more complicated procedure to access Spark and the associated Jupyter notebook but it is only slightly more difficult.
Connecting
- Login to Marc normally as described on [MARC_accounts]
- Start the Jupyter notebook and Spark cluster as a job with something like the following (changing the number of cpus and memory to fit your requirements:
sbatch -N1 -n 38 --cpus-per-task=1 --mem=100G --time=1:00:00 /global/software/spark/sparkOnMarc/sparkOnMarc.sh
Submitted batch job 14790
- The above command will return a job number "14790" in this example. A file named slurm-<jobnumber>.out will be created in the current directory. After a few moments the file will contain the connection information required for you to access a Jupyter notebook that has access to the Spark cluster that was just started.
$ cat slurm-14790.out
<snip -- lots of logging messages that can be ignored unless there's problems>
Discovered Jupyter Notebook server listening on port 54674!
===========================================================================
===========================================================================
===========================================================================
Your Jupyter Notebook with Spark cluster is now active. Inside Putty
You will now need to forward port 8888 to:
sg5:54674
Then you can point your browser started from myappmf.ucalgary.ca to
the URL:
Currently
http://localhost:8888/?token=dccb02273b9be90c833edf658fd3183aa62fa9fabadce6d8
Please see the RCS website rcs.ucalgary.ca for information on how to
access Spark from the Jupyter notebook.
===========================================================================
===========================================================================
===========================================================================
- This message says that the Jupyter server is running on node sg5 on port 54674. Port 8888 needs to be forwarded from the server running Putty to the cluster.
- Click the Putty icon in the upper left corner of the Putty window and select "Change Settings"
- If there's already 8888 listed in the Forwarded ports box click it and click Remove -- the Forwarded ports box should be empty.
- In the Change Settings dialogue box pick "Tunnels" in the left hand box (you'll have to open the Various levels of the tree to get there)
- Enter 8888 into the Source port box
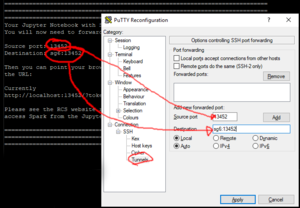
Putty Settings dialogue box showing the required port forwarding. - Copy the circled value from the putty window into the Destination box and click the Add button.
- The "Forwarded ports" box should now contain a concatenation of the text in the source port and destination boxes. i.e. "8888:sg4:54674"
- Click Apply
- Return to the myappmf tab in your browser and start a Google Chrome there. Note: It is important that you use the Chrome from myappmf not your desktop.
- Paste the link containing http://localhost:8888?token= found in the putty terminal window into the browser started from myappmf and you should be rewarded with a Jupyter Notebook session.
In your Python file or terminal load the appropriate python modules and instantiate the cluster:
import os
import atexit
import sys
import re
import pyspark
from pyspark.conf import SparkConf
from pyspark.context import SparkContext
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
conflines=[tuple(a.rstrip().split(" ")) for a in open(os.environ['SPARK_CONFIG_FILE']).readlines()]
conf=SparkConf()
conf.setAll(conflines)
conf.setMaster("spark://%s:%s"% (os.environ['SPARK_MASTER_HOST'],os.environ['SPARK_MASTER_PORT']))
sc=pyspark.SparkContext(conf=conf)
#You need this line if you want to use SparkSQL
sqlCtx=SQLContext(sc)
#YOUR CODE GOES HERE
You now have a sc (Spark Context) and sqlCtx (SQL Context) objects to operate on. Please remember to return to the OOD screen and terminate the Jupyter + Spark app when you are finished.
There are many Spark tutorials out there. Here are some good places to look:
- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/quick-start.html
- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/rdd-programming-guide.html
- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/sql-programming-guide.html
HINT: It helps to google "pyspark" as that returns Python results instead of Scala which is another common language used to interact with Spark.